Category Archives: Theory and Education
What is Stress Relieving and Why We Need It

Stress relieving is a form of post weld heat treatment. In stress relieving we heat a material to a specific temperature; hold it at this temperature for a specified amount of time in order to reduce or eliminate residual stresses; and then cool it at a slow enough rate to prevent these stresses from redeveloping. […]
4 Key Factors Affecting the Fatigue Life of Welded Structures

Designing for fatigue is very different than designing for static loads. One of the biggest challenges is being able to estimate the loads, timing of the loads and duration of the loads. If you look at a bridge you have to estimate the number of vehicles going on the bridge every day, the weight of […]
Estimating the Fatigue Life of Steel Welded Structures and Components
Using S-N curves and formulas from Clause 2 of AWS D1.1
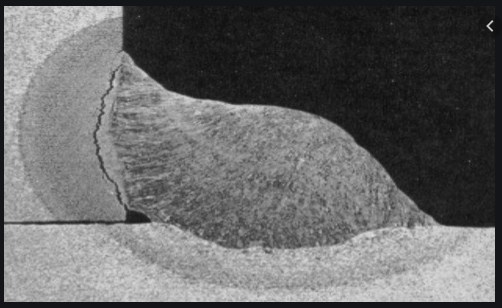
The majority of industrial equipment and welded structural components are subjected to repeated fluctuating loads. These loads are typically of magnitudes that are within the elastic region of the material and well below its yield strength. This means that any deformation of the structure caused by the applied stress will then return to its normal […]
Weldability of Annealed, Normalized, Quenched and Tempered Steels

We frequently receive requests for help developing welding procedures for welding on quenched and/or quenched and tempered steels. Sometimes the call for help is to determine why these steels cracked after welding and how to prevent it from happening in the future. Understanding the supplied condition of the steel you are going to be welding […]
The Reason Behind AWS D1.1 Minimum Fillet Weld Sizes
It's not what you think

Have you ever noticed that there are design rules that prohibit sizing a fillet weld below a certain size for a given thickness of material? If you look at AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2020 Structural Welding Code (Steel) you can find this on Table 7.7. If you happen to own a copy of AISC 360-16 Specification for Structural […]
How Carbon Content Affects the Weldability of Steels
And its effects on strength, hardness, ductility and machinability

Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon along with several other elements in small quantities, all of which have an impact on its properties. Steels can contain varying amounts of carbon and are typically categorized as low, medium or high carbon steels. Low carbon steels are those containing 0.30% carbon or less. Medium carbon […]
6 Reasons Why Metal Fabricators Must Understand Metallurgy

Metal fabricators, or at least those in charge of welding operations, must have a sound understanding of metallurgy. Metallurgy is the study of metals, their properties and their behaviors, especially when undergoing the welding process. Below are 6 areas of fabrication for which an understanding of the metallurgical properties of metals is vital. Material Selection […]
The Advantage of Using Undermatching Filler Metals on High Strength Steels
High strength steels are becoming more and more popular in steel construction. Higher strength means we can reduce the thickness of the base material and thus reduce weight. This is very important not just in vehicles but in static structures as well. However, higher strength steels usually bring about a few issues that if not […]
What is Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)?
What is it? Why is PWHT needed? How is PWHT done?
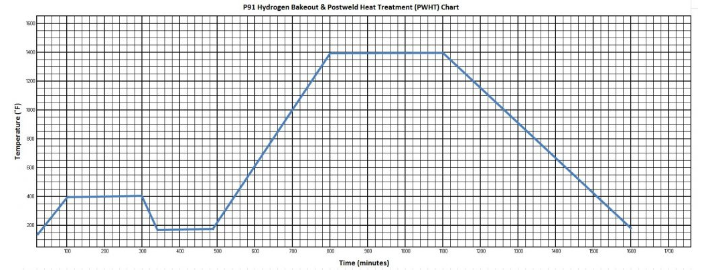
Have you heard of post weld heat treatment (PWHT)? Of course you have. If you are involved in welding you have definitely heard this term. But what is PHWT? When is PWHT required? What temperature should PWHT be done at? Heat treating of materials can be a very complicated subject, but when it comes to […]
